9 min read

Financial reports are necessary and legally required of businesses, so everyone uses them. Unfortunately, many business leaders choose not to generate management reports, mistakenly believing that they are irrelevant to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
|
Key Takeaways
|
This, however, is a misconception that can have serious consequences. Management reports are relevant and important for businesses of all sizes and types. Generally, if your business is large enough that you can't keep track of every aspect of it in your head, then your business is large enough to benefit from management reporting.
Fundamentally, management reporting enables the continual improvement of every aspect of a business. It helps business leaders make the right decisions at the right time. It also helps business leaders to improve workflow, efficiency, and operations overall. Better, data-driven decision-making also helps to improve productivity, business strategy, profits, and financial health. This helps SMEs avoid pitfalls, overcome challenges, and take advantage of opp
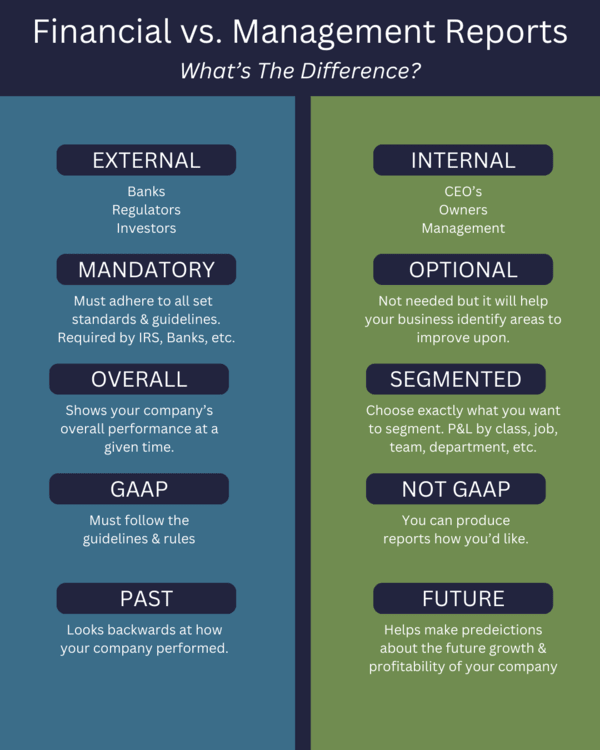
What's the Difference Between Financial Reports and Management Reports?
Financial Reports
What They Are
Financial reports are basic, historic reports of a company's financial data. They include the balance sheet, income statement (also called the profit and loss statement), and the statement of cash flow.
How They're Used
Financial reports display a bird's eye view of a business's past financial data over a set period of time. They're primarily used for external purposes, such as:
- Compliance and satisfying financial accounting standards
- Providing financial information to suppliers and vendors
- Credit requests with bankers, creditors, or other lenders
- Communicating financial data with company stakeholders such as investors and board members
Since financial reports display historical, financial data, it isn't necessarily advisable to use them for strategic decision-making purposes.
Read More: How Much Should Mid-Market Companies Pay For Outsourced CFO Services?
Management Reports
What They Are
Management reports are based on a company's current financial data, and sometimes, they also contain additional data compiled from various departments within a business. Management reports are more dynamic than financial reports. Often perused alongside the company's most recent financial reports, management reports include the reports that are helpful for decision-making and the strategic management of the business (or any specific audience). There are no rules, regulations, or standards governing management reports, so your company's list can include any reports or key performance indicators (KPIs) that you find useful, helpful, and meaningful.
Some examples of management reports include:
- Profit and loss by class
- Budget reports (budget vs. actuals)
- Cash flow forecast
- Trailing-twelve-month charts
- A list of outstanding invoices from creditors and debtors
- New business pipeline and analysis
- KPI data and trends (profit margins, ROI on labor, customer acquisition costs, customer lifetime value, days sales outstanding, etc.)
How They're Used
Management reports are used internally for management purposes. Rather than focusing on evaluating past performance (like financial reports), management reports focus on the business's current numbers and future projections.
Often using real-time data, management reports help business leaders make decisions to improve the leadership, management, operation, efficiency, and productivity of a business. They can help business owners identify future challenges before they become a problem and put effective strategies into place to mitigate potential risks. They also make it possible to spot opportunities as they arise and make data-driven decisions about the best ways to leverage the company's assets to take advantage of those opportunities.
Financial Reports vs. Management Reports: What’s the Difference?
7 Management Reports Best Practices for SMEs
1. Use Accounting Software That Supports Management Accounting
Most business leaders look at management reports on a monthly basis. Others choose to keep a closer eye on their numbers with weekly or even daily reporting. (More frequent evaluation can be especially useful in times when you might find your company in a precarious financial position requiring close attention and exceptionally careful management.)
Management reporting, especially more frequent management reporting, relies on the availability of real-time data. This means your business should choose an accounting software that supports daily updates and account closings, rather than only updating data at the end of a financial period.
Accounting software that helps facilitate management accounting and reporting is typically cloud-based such as QuickBooks Online or Sage Intacct. These options can help to ensure your financial data is collected, compiled, and organized on a daily basis for up-to-date management reports that are available at all times.
2. Integrate With Organization-Wide Applications
For accounting software to function as a complete management accounting tool, it is necessary to integrate additional applications into the software you're using so that it can truly generate management reports with comprehensive data fields that span your organization.
For example, integrating accounting software with employee time-tracking tools is essential for generating profit and loss statements by class. This simple integration gives you the ability to analyze the profitability of every aspect of your business from client and job types to departments and employees.
Both QuickBooks and Sage Intacct fully integrate with long lists of popular and highly useful applications that can help you improve operations, efficiency, and profits throughout your company.
3. Rely Heavily on Automation
For many businesses, the primary roadblock to successful management reporting is manual processes. Manual processes slow the availability of real-time data. They also cloud the data with human error and inaccuracies. As a result, businesses that are not relying heavily on automated processes - especially in their bookkeeping and accounting systems - won't be able to use or benefit from management accounting and reporting as successfully as those that have automated as many processes as possible.
4. Make Management Reporting a Habit
While management reporting can provide you with singular data points that are useful and informative, your financial data is more valuable and informative if it can be understood in terms of trends. Seeing trends in data requires you to be in the habit of generating management reports and looking at them on a regular basis.
While looking at management reports quarterly can provide some insight, it's typically more useful to evaluate your management reports on a more frequent schedule, such as monthly.
Read More: Outsourced Accounting Costs for Mid-Market Companies
This can help you quickly identify changes, as they occur rather than after the fact, and implement strategies to solve problems or leverage opportunities. As you make changes in your business, you should be able to measure and see the effects right away in your management reports. You can then evaluate the success of the strategies you implement and make adjustments for further improvements.
In order for this cycle of strategy, implementation, measurement, evaluation, and adjustment to be useful and successful, business leaders must be in the habit of generating and reading management reports.
5. Use the Right Reports for Your Business
There are actually countless more management reports and metrics available than you actually need to use in your business. Your financial and operational data can be combined in many different ways to measure the performance of every aspect of your business from a variety of different perspectives.
Attempting to measure and evaluate all of this data is overwhelming and unnecessary. Focusing on the wrong data or too much data will waste time and distract you from the numbers that are truly important to your business.
Narrow down your management reporting to the charts, metrics, and KPIs that are relevant to your specific business, industry, productivity, employees, profit drivers, and goals.
6 KPIs to Drive Profitability in Your Business
A guide to help you read and interpret Company and People KPIs [DOWNLOAD]
6. Set SMART Goals and Create an Operating Framework
If you're struggling to narrow down your management reports and metrics to those that are most relevant to your business, then you likely do not have a clear enough picture of your business's goals, benchmarks, and operating framework.
Establishing SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound) goals in your business will help you improve, manage, and grow more intentionally.
Do you have a future vision for your business? Think about where you want your business to be five years from now and put that into concrete, measurable terms (for example, 5% or 10% growth or a specific figure for profit margins). This gives you your time frame and specific goal. Divide the goal by five and you have your annual benchmark. Divide that by twelve and you have a monthly benchmark. Next, think about how you can achieve that goal and how you can measure your progress toward it. That strategy, those benchmarks, and your performance KPIs can now be worked into an operating framework for business success.
Read More: Unlock Business Growth With Written Goals
7. Lean on Outsourced Accounting Services
While SMEs stand to benefit greatly from management accounting, it can be difficult to implement the tools, technology, processes, and procedures that are necessary for management accounting in an SME. Due to limitations on resources, building a complete, high-functioning back office in-house can be unaffordable for most small and medium-sized businesses. As a result, they wind up relying on a piecemealed back office to generate unreliable management reports.
SMEs, however, can rely on outsourced accounting services such as outsourced bookkeeping and accounting in addition to outsourced controller and chief financial officer services to facilitate, implement, and assist with the management reporting process. Additionally, an outsourced CFO can help you learn to read, understand, and use your management reports to make data-driven decisions designed to strengthen the company.
Power Your SME With a Smarter Back Office and Financial Insights Designed for Business Leadership
In an SME, a smarter back office is an outsourced back office. Through the power of outsourcing, your business can benefit from powerful tools and technology in addition to a highly experienced back-office team. With these resources, you can rest easy knowing that your financial reports are correct and compliant while beginning to lead your business with increased confidence thanks to the financial insights gained through reliable management reporting.

.png?width=563&height=144&name=New%20GF%20Logo%20(37).png)


